Like WordPress, SEO has its own technical jargon. In the course of articles or videos, you may have read or heard the following terms: backlinks, crawl, long tail, black hat, etc.
Even this intimidating expression: cannibalism. And no, I reassure you: Google does not eat the arms or legs of SEO enemies.

SEO is also about pillars (we’ll come back to that). One of them is on-page SEO, another jargony expression. Do you want to know more about it?
This complete guide will explain it all to you. In particular, you will discover 16 techniques for on-page SEO that you can easily apply on WordPress, even if you’re a beginner.
By the end of this guide, you’ll be able to improve your content’s search engine ranking. You’ll also have a better chance of getting more traffic. Ready to go? Let’s get started.
Overview
What is on-page SEO?
Definition of on-page SEO
On-page SEO is a search engine optimization practice that consists of optimizing the content of a site (posts and pages) in order to improve their positioning in the results of search engines like Google.
In technical jargon, it’s referred to as both on-page SEO and on-site SEO. On-page optimization takes into account both criteria in your content that’s visible to the Internet user as well as criteria invisible on the screen, which is contained in the HTML source code.
For example, it involves the optimization of the following elements:
- Title and meta-description tags
- Keyword density and use in strategic places (hn titles, URL, title tags, and meta-description tags)
- Content
- Images
- Loading speed and user experience (UX)
- Internal and external links
- Etc.
Throughout this article, I will talk primarily about Google, because it’s the search engine that Internet users in the United States use the most. With 88.7% of the market share, it crushes its two closest competitors Bing (6.6%) and Yahoo! (2.4%).
On-page SEO, off-page SEO, and SEO pillars
When we talk about Search Engine Optimization (SEO), we usually talk about on-page SEO and its complementary partner: off-page SEO.
What exactly is off-page SEO? Off-page SEO refers to SEO optimization that takes place off-page, rather than directly on the content, with one objective: improving the ranking of a page or an article on a search engine.
The main technique for off-page SEO is the construction of backlinks. These are inbound links made by another site to yours.
Roughly speaking, the more backlinks you have in relation to your site’s theme, the more authority and popularity you gain with Google, which will then be more inclined to better position your content in its search results pages.
If we broaden our perspective, on-page SEO is part of what is more commonly known as the “pillars of SEO.” Traditionally, there are three levers of SEO:
- On-page SEO.
- Off-page SEO.
- Technical SEO, which refers to the optimization of the structure of your WordPress site. The idea here is to make it easier for search engines to crawl and index your content. With WordPress, you already have a good technical base, but you still need to properly configure the no. 1 CMS (Content Management System) on the market and optimize your theme. Otherwise, you risk having useless pages, duplicate content, or bad URLs.
Why is on-page SEO important?
To rank a page in its search results — a search engine positions a page and not an entire site — Google’s algorithm is based on about 200 regularly updated criteria.
Its objective is to provide the most useful answer to the user’s query (keyword or group of keywords typed in the search bar).
One of the most important factors for Google in determining the results returned for your query is the relevance of the content.
To evaluate this, it takes into account the presence of keywords scattered throughout the content. As Google explains, “if those keywords appear on the page, or if they appear in the headings or body of the text, the information might be more relevant.“
Hence the importance of working on your on-page SEO! Overall, optimizing all three pillars of SEO is essential if you want to attract more traffic to your site.
If you increase your number of monthly visits, you will have more opportunities to multiply conversions (newsletter registration, form filling, product purchase, etc.) and to increase your turnover.
Now, after having covered the theoretical background, let’s get down to business with a list of 16 practical techniques to effectively improve the on-page SEO of your WordPress site and get results.
To learn more about the pillars of SEO and how search engines index your content, check out our comprehensive SEO guide.
16 ways to optimize the on-page SEO of your WordPress site
Use an on-page SEO plugin
To start optimizing the on-page SEO of your WordPress installation, I recommend that you first install an SEO plugin.
All the most famous ones in the official directory have options to help you improve your content (main keyword density in the text, readability, internal linking, etc.) and to set on-page criteria directly on your admin interface.
Thanks to whichever one you use, you won’t need to go into the source code of each page or post to write your title and meta-description tags (we will come back to this later in more detail).
There is certainly no shortage of SEO plugins in the WordPress plugin directory. You probably know:
If you haven’t found the one yet, here are some tips to help you decide:
- Find out about the features offered by the plugin you are interested in and make sure they match your needs.
- Take advantage of the free version of the plugin to form a first opinion and see if the plugin suits you. If you’ve already configured some settings, don’t panic: most popular SEO plugins offer options to import data from another SEO plugin.
- Choose a plugin that fits your profile. Yoast and All-in-One SEO are easy to learn: they will appeal to beginners. SEOPress and Rank Math offer more advanced options for a more SEO-savvy audience.
For your information, WPMarmite uses Yoast SEO. We offer a complete guide to learn how to configure it. You can also check out our test of 6 SEO plugins.
If you want to effectively improve your site’s natural referencing, I recommend you use a tool dedicated to keyword research. Among the best known on the market, you will find Semrush and Ahrefs. Their free version, although limited, can still help you if you’re just starting out (Semrush even offers a tool dedicated to on-page SEO called On Page SEO Checker).
Also rely on the free tools offered by Google, especially the Google Search Console, which can help you with some on-page SEO actions.
Create quality content to improve on-page SEO
Have you activated an SEO plugin? That’s great. You have a solid foundation for optimizing the on-page SEO of your content. But first, you’ll need to create the content!
To have a chance of being visible in a good position on Google, you’ll have to create an article or a page that stands out from the crowd.
This means writing original and high quality content, according to Google. Your content must meet several criteria:
- It must be reliable and based on some level of expertise.
- It must be useful to the reader, for example by providing a clear and precise answer to a problem she is facing. Its added value must be tangible.
- It must be original: you can’t just copy and paste right and left things that you’ve read, in order to avoid the creation of duplicate content.
- It must be relevant. As we have already seen, this requires the well-targeted use of a main keyword and its synonyms.
- It must respond to a search intention, i.e. the reason why an internet user enters a query. Sometimes, she’ll want to find out information about something (e.g. a camera of a specific brand). At other times, she’ll just want to buy it.
If you follow these instructions to the letter, you won’t do too bad. 😉 And Google will eat out of your hand because you will meet the criteria of what it calls E-E-A-T: expertise, experience, authoritativeness, and trustworthiness.
Paying attention to search intent
Even if you design high-quality content, don’t neglect the fundamental notion of search intent. If you don’t meet it, you won’t be able to rank high on the first page of Google.
Here are several tips to detect the search intent and respond to it as best as possible:
- Type your main query (keyword) into the Google search bar and see which results come up first. For example, if I type “seo tool” on Google, I see that the best positioned results are blog posts. To have a chance to compete with them, I should start with this type of content.
- Analyze the SERP (search results page) to see what content format is the most used. In my example, I noticed that all the posts without exception offer a list of the best SEO tools with a detailed presentation each time. Don’t reinvent the wheel: do the same thing… but better. For example, offer a presentation of more tools than what the competition does.
- Within your content, answer the questions of the users. What do they want to know? What are they looking for? Again, build on what your well-positioned competitors are already doing. Study their subheadings and see which ones are used in multiple articles at once with the Ahrefs SEO Toolbar browser extension.
To make writing your content easier, design a detailed outline beforehand with your main parts and sub-parts, for example using a free collaborative tool like Google Docs.
Make the content readable
If your content is relevant and meets the search intent, you will increase your chances of being well positioned on Google against your competitors.
As long as you don’t ruin it by proposing indigestible and unreadable content, however, which would make your bounce rate soar. This would send a bad signal to Google.
To keep your visitors comfortable on your pages, use the following tips:
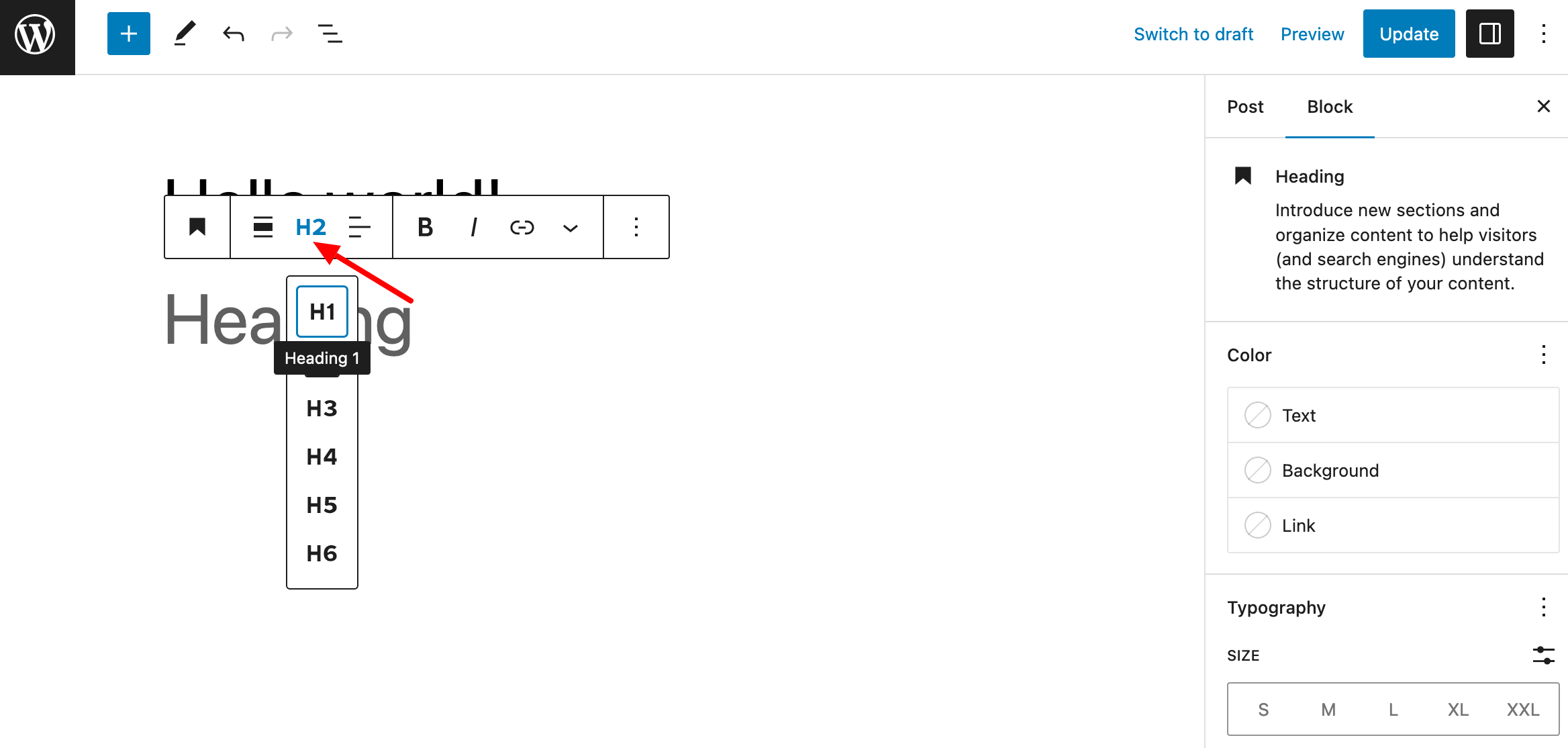
- Use subheadings (h2, h3, and h4 tags) regularly to prioritize your content. In the WordPress content editor, use the “Heading” block to do this:
- Skip lines and develop one idea per paragraph. When reading, as soon as you feel like you’re reading a block of text, skip a line.
- Use bulleted or numbered lists to detail your ideas.
- Add images and/or videos whenever possible to illustrate your points. There’s no rule for this, but you can try to include them every 200 to 300 words.
- Highlight important passages or words by adding bold.
- Keep sentences short.
- Write in the active voice and address your reader directly by using the pronoun “you.”
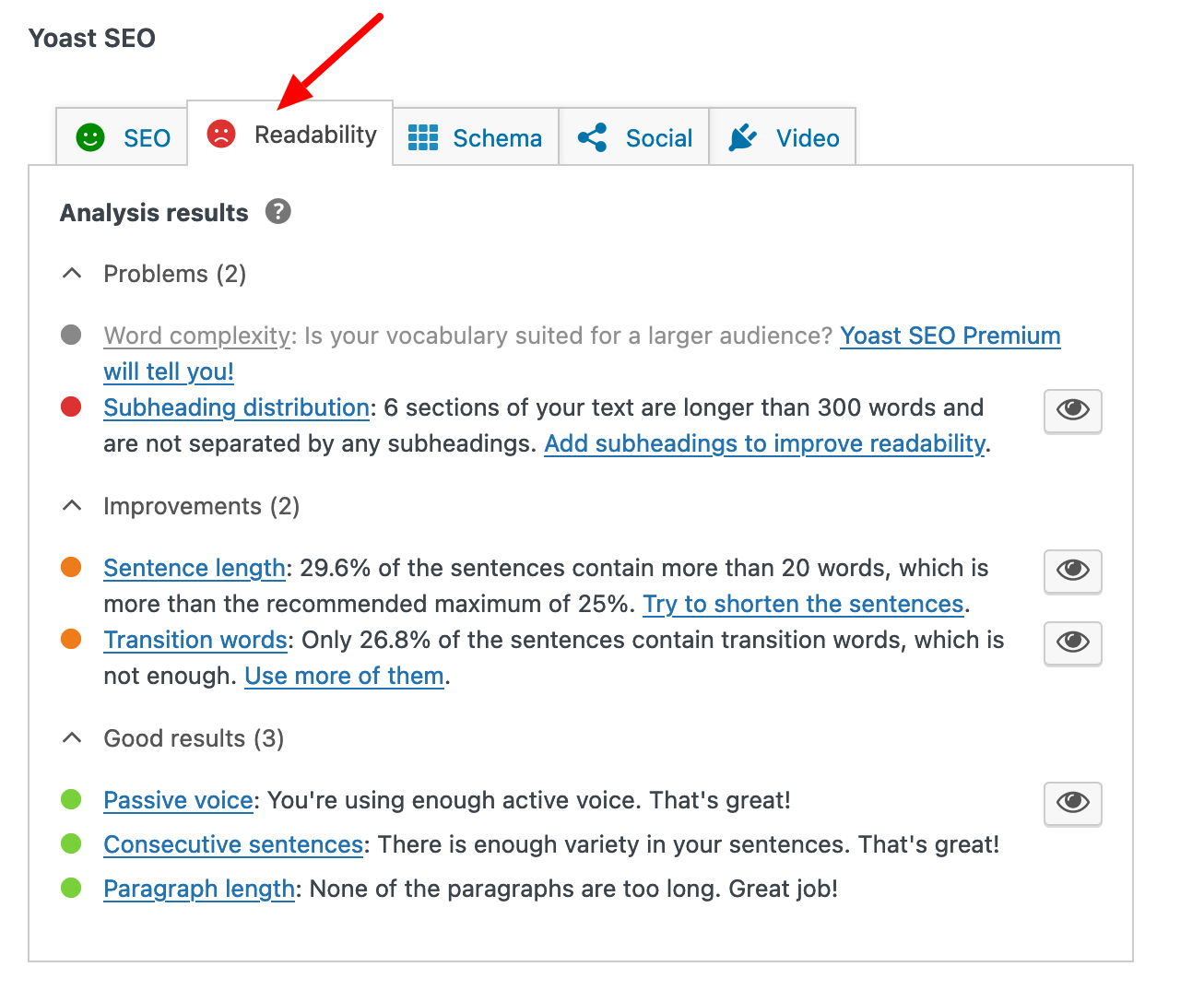
Several SEO plugins offer recommendations for improving the readability of your text. If you use Yoast SEO, go to its dedicated box at the bottom of your post or page, on the WordPress content editor. In the “Readability” tab, you will have an automatic analysis of your text, with color-coded areas for improvement (green dots indicate that the recommendations have been followed).
Optimizing your page around a main keyword
Remember: Google relies heavily on the presence of keywords on your page to evaluate the relevance of your content.
Here are some basic rules to follow to do things the right way. First, integrate your main keyword in several strategic areas:
- The title of your article or page (h1 tag). If your theme is well designed, your titles will automatically be in an h1 tag.
- Your introduction. Put your main keyword in the first 50 to 100 words of your content.
- The slug of your URL
- Some of your subheadings (e.g. h2 or h3) but not all, to avoid over-optimization
- Your content. Google doesn’t set a precise rule on keyword density, i.e. how many times you should use it in a text. Just add it from time to time, without overdoing it. Yoast SEO will tell you if you use it too much or too little depending on the length of your text:
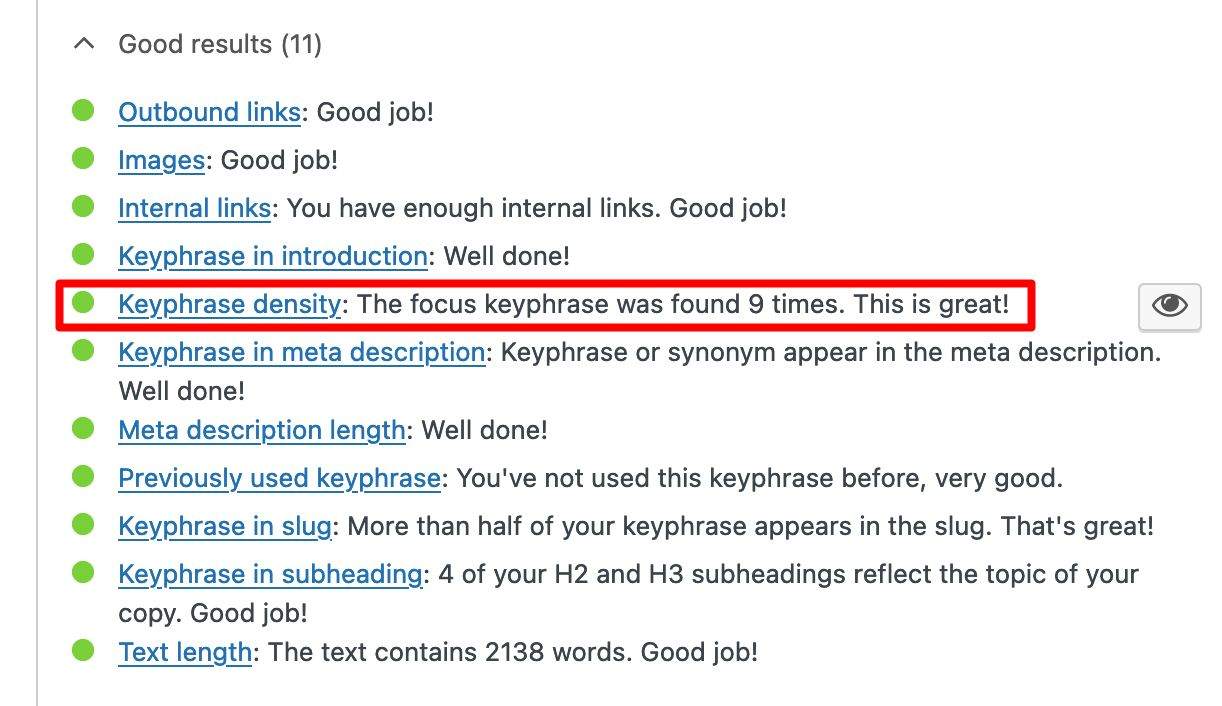
Before publishing your content, check that your keyword seems natural wherever it’s present on your site. If it’s repeated too frequently and inappropriately — especially out of context — Google indicates that this can “harm your site’s ranking” and it could penalize you.
To avoid this, use semantically related words. To find them, rely on Google’s related searches or on dedicated premium tools like Yourtext.guru or Text Optimizer.
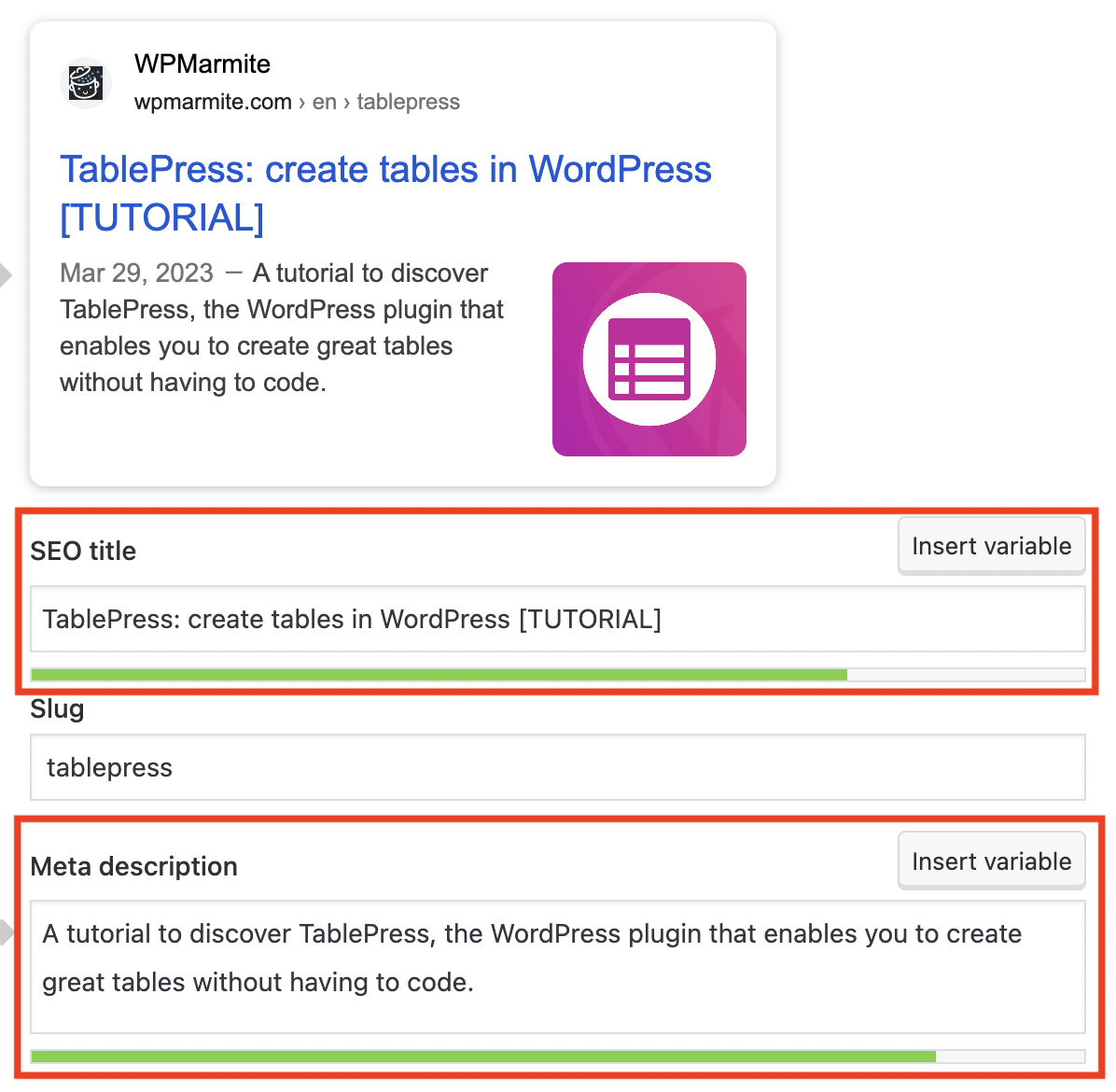
Perfect the title and meta-description tags
Your main keyword must also appear in your title and meta-description tags — these are very important in SEO (especially the title tag). A quick definition, before going further:
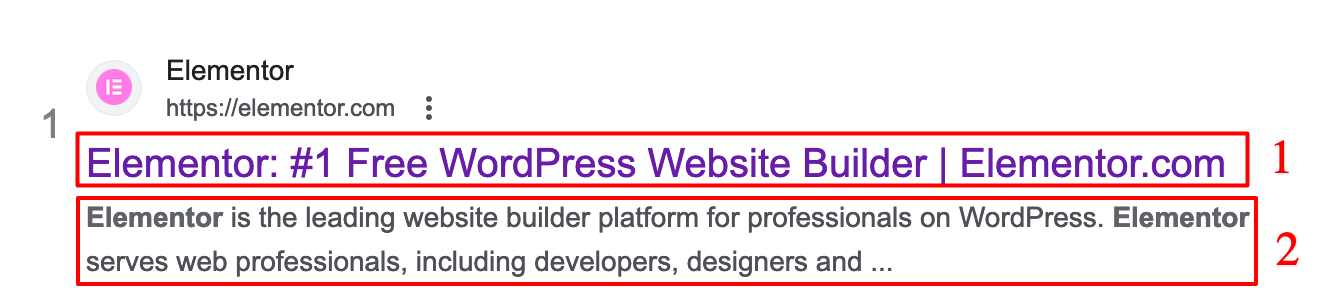
- The title tag is the title of a result on the Google search page. For example, the
titletag in the example below is: “Elementor: #1 Free WordPress Website Builder | Elementor.com” (number 1 in the picture). It should not be confused with the h1 tag, which includes the title of your page or article. - The
meta-descriptiontag offers Google and Internet users a summary of your page (number 2 below):
Now that you’ve gotten to know these two tags, it’s time to optimize them with these tips:
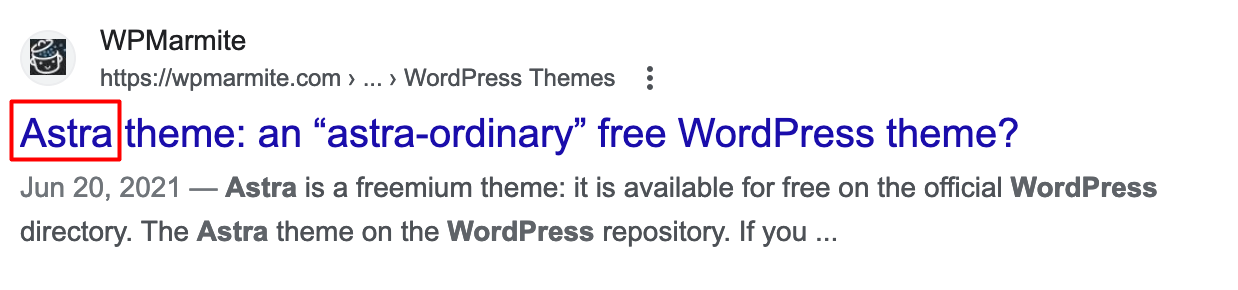
- Add your main keyword to each of them so that Google understands what your content is about. If it’s possible, and sounds natural, integrate your main keyword at the beginning of your
titletag, like here (the article is optimized around the keyword “astra”):
- Be careful with their length! If you don’t want them to be cut off on the screen, don’t exceed about 70 characters for a title tag and 156-158 characters for a meta-description tag. But beware, Google can also change its standards in terms of length from time to time. To be sure you’re not mistaken, rely on the indications offered by your SEO plugin. Or use a free SERP simulator like those proposed by Mangools or Ranktracker.
- Create unique title and meta description tags for each page.
Use a clean URL
When it comes to on-page SEO, it’s also important to optimize your URLs, i.e. the address of your web pages. For this, I advise you to:
- Prioritize a short and descriptive format to facilitate the understanding of the Internet user. This will give you a better chance of multiplying your click rate.
- Include your main keyword in the slug of your URL. For example, our guide to Elementor is optimized around the following keyword: “elementor.” The slug of its URL is, therefore, logically… elementor.
If your URL is too long, Google may also cut it off in its search results. This can have a negative impact on your site’s traffic.
On WordPress, optimizing a URL is very simple. Before publishing content, you just have to click on the link next to the word URL, and enter the text of your choice:
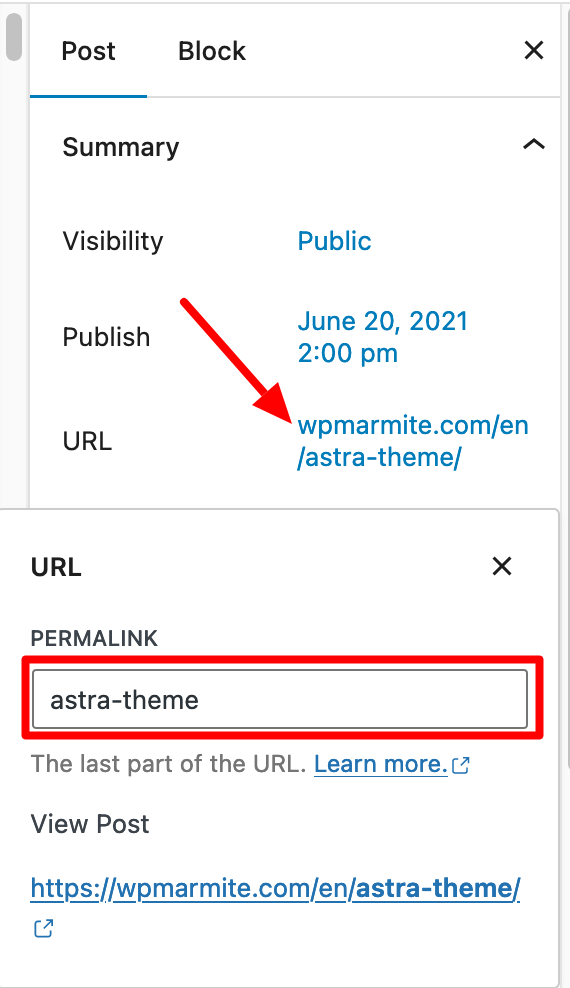
When writing your slug, it’s important to:
- Use lower case instead of upper case
- Use hyphens to separate the terms of your slug
- Avoid special characters (accents, symbols, etc.)
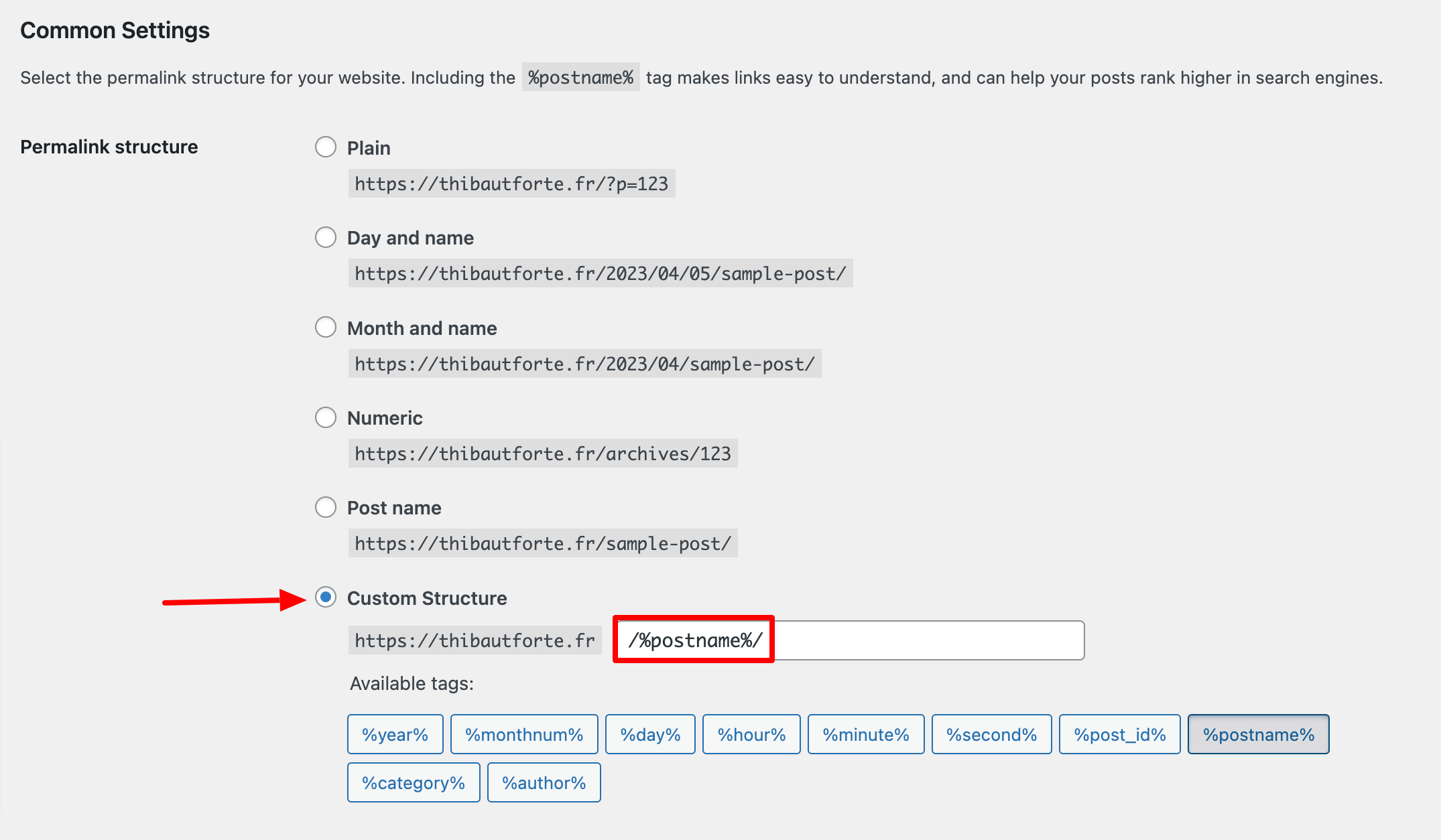
By the way, take the opportunity to adopt a clean permalink structure in Settings > Permalinks, on the WordPress administration interface. For SEO purposes, the cleanest structure is based on the post name.
Choose this setting as soon as you install WordPress. If you change the structure of your permalinks later, beware of possible 404 errors. If this happens to you, redirect the problematic URLs with the Redirection plugin.
Optimize images
While many on-page SEO actions are related to textual content, images also have their role, if I may say so.
In fact, optimizing the SEO of your images can help you rank better on Google Images (which allows for image searches), and in turn, increase traffic to your WordPress site.
If you feel like it, do the following on the images you upload in your Media Library:
- Give them a short and descriptive name. For example, red-polar-cover.jpg rather than img987623.jpg.
- Fill in the alt tag (alternative text) for each of your photos, to improve accessibility and to help Google determine the purpose of your image.
- Choose the right file format (jpg, png, gif, webp, etc.). For example, PNG handles transparency, JPG does not.
- Reduce the size and weight of your images using a plugin like Imagify.
Work on the internal linking of your content in on-page SEO
It’s impossible to talk about on-page SEO without mentioning the issue of links. We’ll cover that now. Let’s start with internal links.
This is when you link to other publications on your site or blog. Including internal links lets you send your visitors to content that’s related to what they are already reading, while keeping them on your site. This way, you limit the bounce rate.
Here again, there are no rules about the minimum number of links to add to a page. Use common sense: if you feel that a resource provides additional value to your reader, create an internal link. It’s that simple.
You can also use internal links to “push” a page that lacks its own authority to try to gain positions on the SERP.
To do this, create an internal link to it from a page of your site that receives a lot of traffic.
To go further and improve the internal linkage of your content, you can also use the plugins below:
- WP-PageNavi, to set up a navigation in the form of page numbers (instead of Previous-Next). This will help search engines and your visitors to better find their way around.
- Your SEO plugin, if it offers an option to suggest related articles at the bottom of each of your posts. If not, you can activate the YARPP plugin.

Creating external links
After the internal links, it’s time for external links. This is when you link to third party sites.
It’s useful to slip in a few external links to lend credibility and support to your words, while giving your readers access to your sources. Google will then see you as a reliable resource, and you know that’s a good sign. 😉
If possible, prioritize external links to authority sites (Wikipedia, journalistic media, etc.). The logic is the same as for internal links: if it helps the user and brings added value, link to an external site.
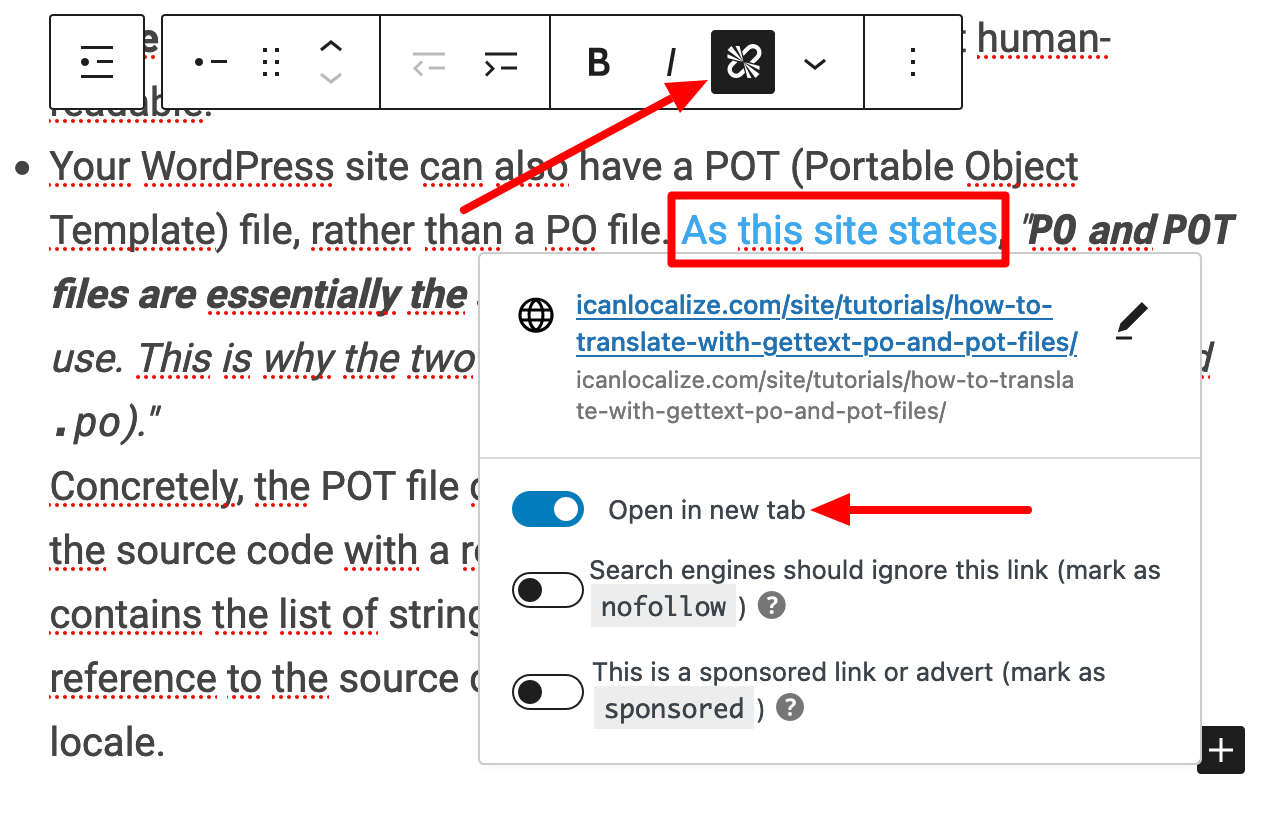
To avoid a visitor leaving your site permanently by following an external link, set it to open in a new tab. To do this, select the piece of text of your choice in the WordPress content editor. Then click on the link icon. Finish by activating the “Open in new tab” button. This way, your visitor will always have the tab of your page open.
Pay attention to the loading speed and the mobile ergonomics
The loading speed and mobile ergonomics, which we will now focus on, can be considered primarily as criteria related to technical SEO.
However, Google indicates that its search algorithms also take into account the ease of use of web pages in its ranking, by evaluating the loading speed and mobile usability in particular.
This is what it calls the Page Experience Signals, which include the famous Core Web Vitals.
Specifically, “where there are many pages that may be similar in relevance,” Google says that “page experience can be much more important for visibility in Search.”
So you need to pay close attention to this by optimizing the on-page SEO of your content (but prioritizing the quality of your content over the on-page experience).
As for optimizing your loading speed, I refer you to our guide that details 10 steps to speed up WordPress.
Regarding mobile ergonomics, it’s important that your pages are displayed perfectly on all screen sizes, from computer to smartphone. This is called responsive design.
This requires the use of a theme designed to be responsive. This is now the case for the vast majority of those you will find on the official directory, like the excellent Astra, Neve, Kadence, or Blocksy.
Finally, think about checking the responsive display of your content with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test (free).
Use structured data
Trying to increase your click-through rate? I’m guessing yes (who wouldn’t?). To do so, you can rely on what’s called structured data.
Structured data is information present in the HTML code of your page in the form of semantic tags, mostly from a vocabulary called Schema.org. These tags help Google to better understand the meaning of your page’s content.
Even more pertinent, this structured data allows you to display rich snippets on search results pages.
Rich snippets give the user access to additional information about a search result. For example, for a recipe, he will see the prep time, reviews, etc.:
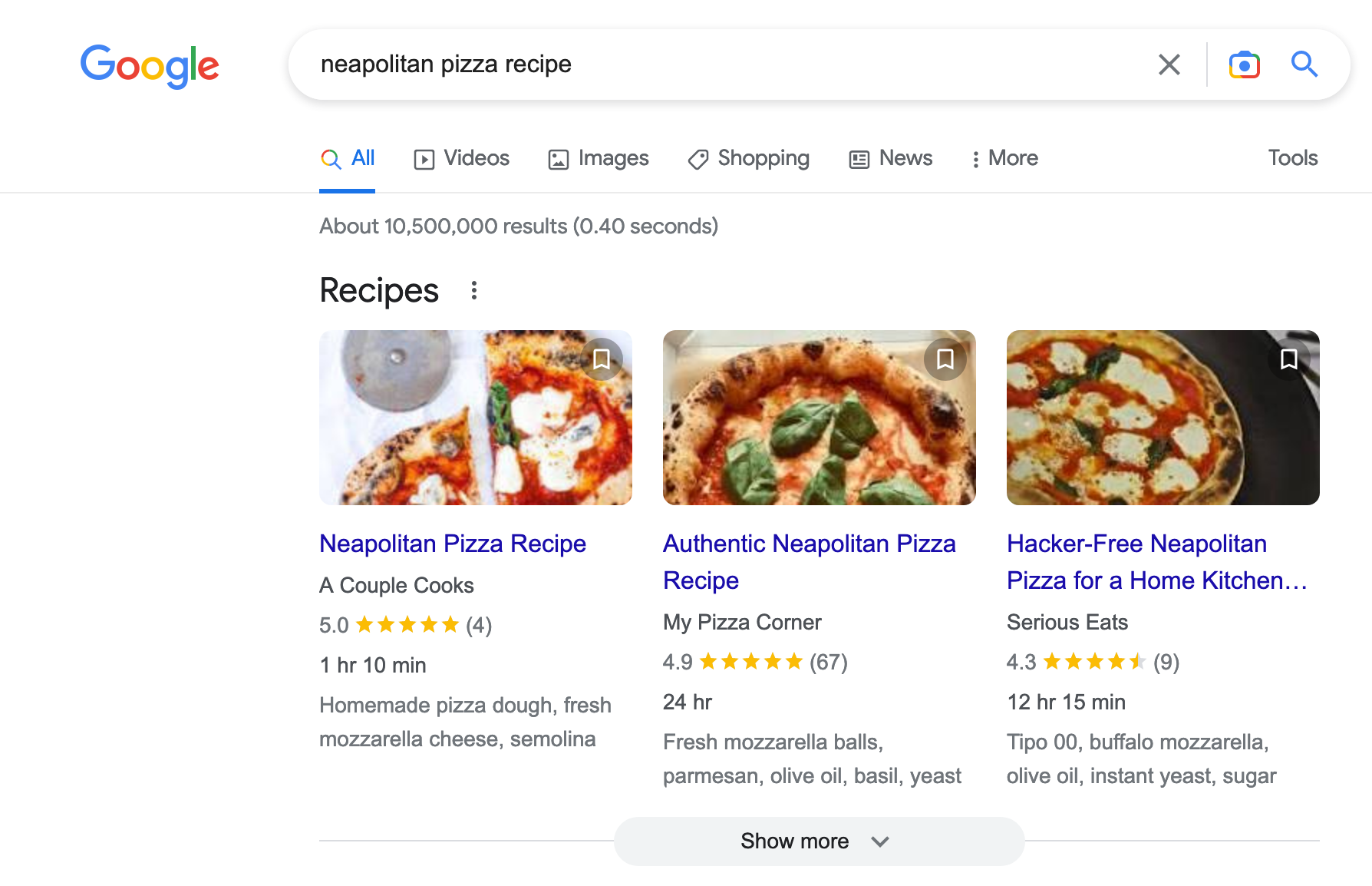
Recipes are just one example. You can also use rich snippets to highlight events, reviews, products, companies, people (e.g. singers), etc.
To add structured data to your WordPress site and give your on-page SEO a boost, you don’t need to get your hands dirty.
General SEO plugins like Yoast, Rank Math, and SEOPress Pro will automatically do this for you on your posts and pages.
Try to position yourself in featured snippet to boost your on-page SEO
Since we just talked about rich snippets in your on-page SEO strategy, let’s talk about its false twin: featured snippets. It’s easy to confuse the two terms, which are actually unrelated.
A featured snippet is an insert located at the very top of the Google search results page. It gives a short answer to a question asked by the Internet user and is generally presented in the following forms: paragraph, list, table, or video.
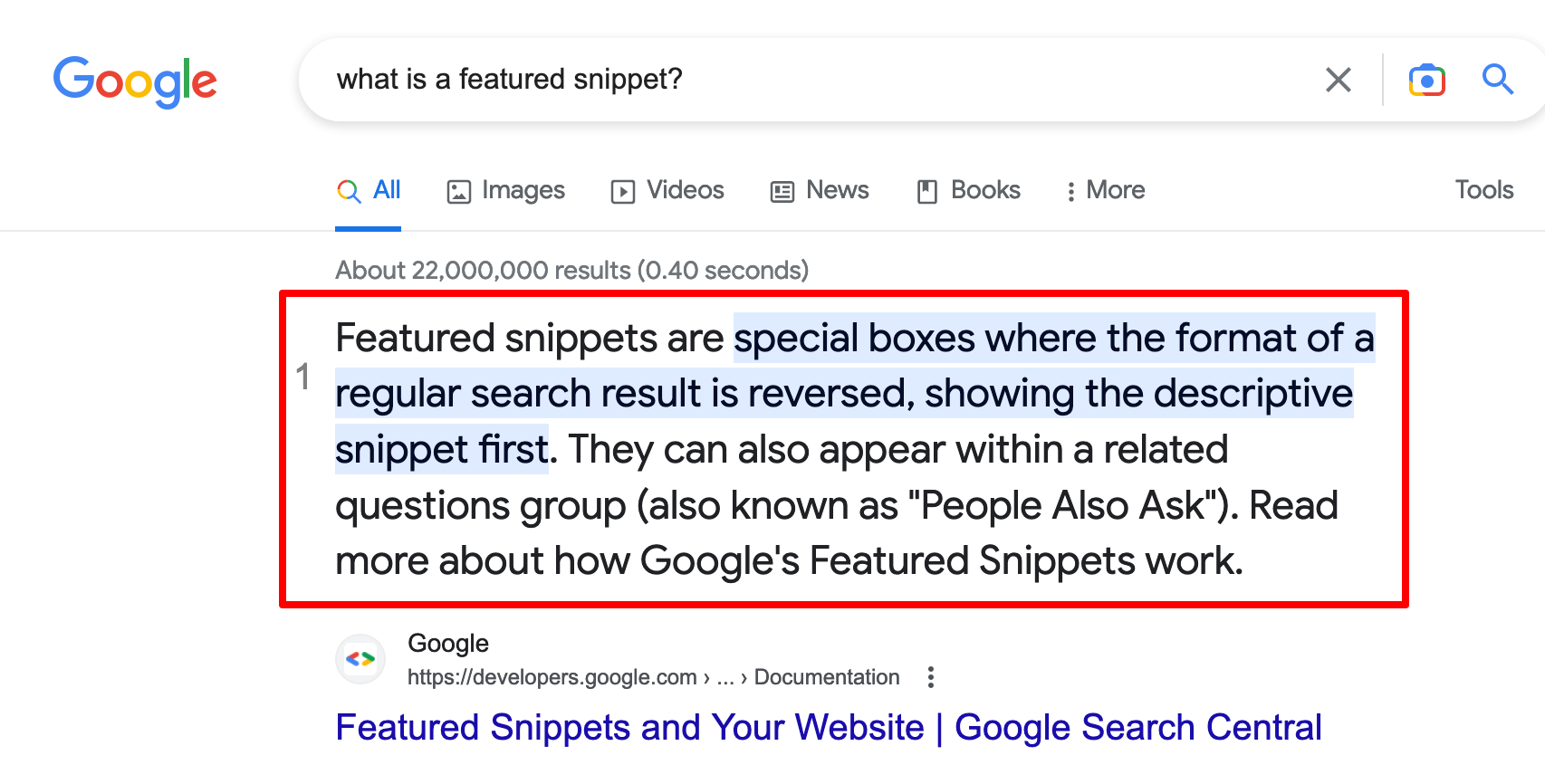
The main value of the featured snippet is its visibility: it will appear in the first position on the results page. And as the first result is on average the one that is most clicked on the SERP, well, it can bring you additional traffic.
To try to appear in the featured snippet, follow the tips below:
- Check if Google already offers a featured snippet for the question you want to answer. For example, if you want to explain what the Beaver Builder page builder is, type in Google: “What is Beaver Builder?” You’ll see that there is already a featured snippet, from the Beaver Builder website:
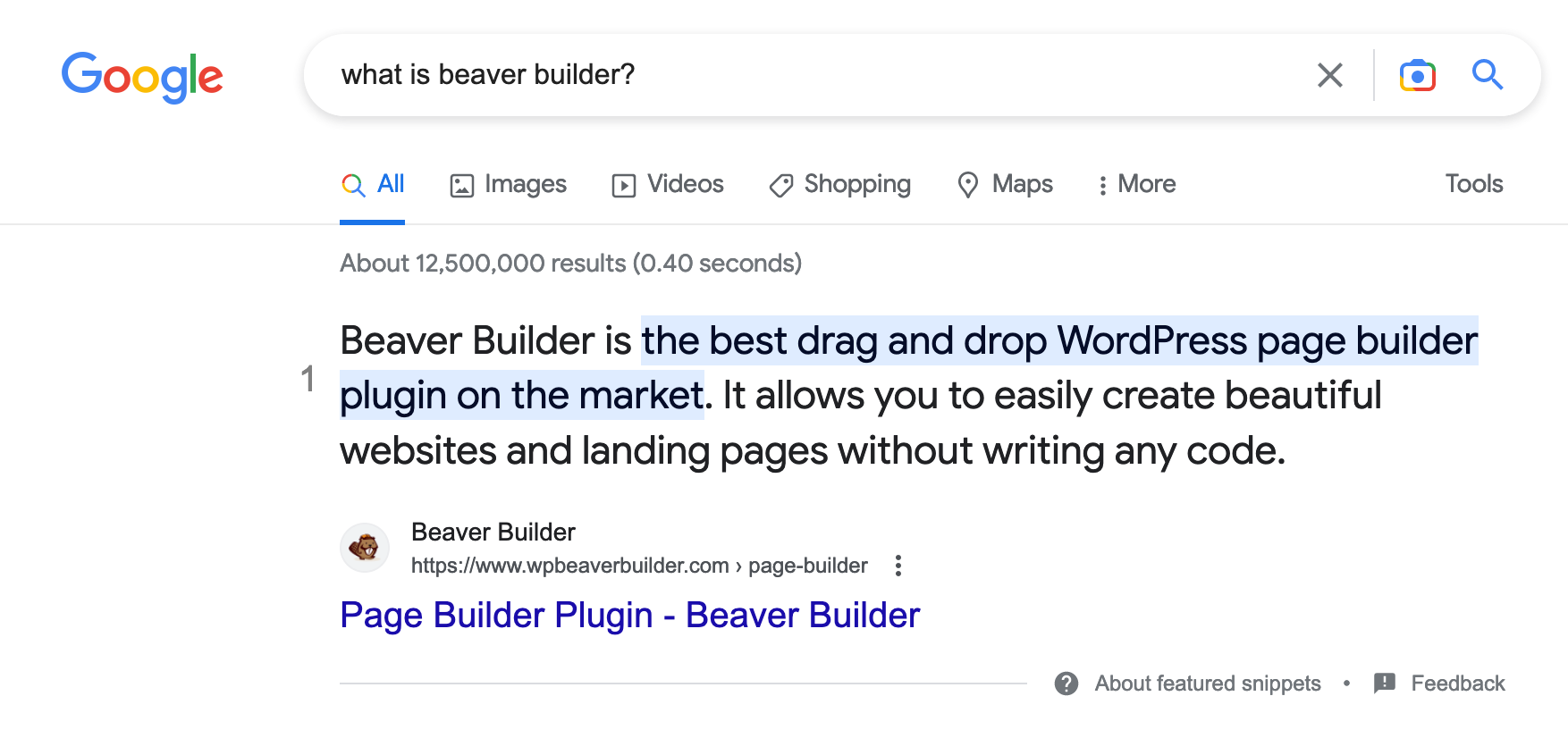
- To do this, you must add a question and its answer in your content (e.g. in an article on Beaver Builder).
- Prioritize an article that’s already well positioned, if possible in the first five positions of natural search. If you are not yet on the first page of Google, forget it: the search engine won’t use your content in the featured snippet.
- Choose the right featured snippet format. In our example on Beaver Builder, we see that Google has a paragraph. So write a paragraph, not a video. If Google displays a list, create a list in your content.
- Be concise. The ideal length of a featured snippet in paragraph format would be 40 to 50 words, according to this study.
Pay attention to your comments
Once you have implemented all the tips listed in this article, chances are that more and more readers will interact with your content.
To that end, some of them will leave you comments to extend the discussion. A constructive and well-moderated comment area can strengthen your on-page SEO work.
Particularly because if a user spends extra time on your content, chances are you will limit your bounce rate.
In addition, relevant comments can also add value to your content if they offer additional solutions not mentioned in the article.
To have a great comment area, I recommend the following:
- Include a call to action at the end of your articles to encourage your reader to leave a comment. This can give them a push if they are still hesitant to share their opinion.
- Reply to relevant comments and delete those that are not relevant.
- Publish comments that are critical, if they are constructive. This will show that you are open-minded and will give you a chance to provide a well-founded answer to the criticisms you receive.
- Moderate comments upstream using a plugin like Akismet to limit spam.
- Add a comment policy, if needed, to give some guidelines (minimum length of a comment, prohibition of outrageous comments, etc.).
Test, test, and test again
To finish this article, I finally advise you to conduct your own on-page SEO tests at home.
You shouldn’t always follow the letter of what Google recommends, which sometimes adopts a double standard.
A good example is the creation of content generated by artificial intelligence. In the spring of 2022, Google stated that texts created by AI were against its guidelines. Therefore, sites that use such techniques could lose their position in the search results.
However, in practice, you will find many testimonies of site editors on social networks that have managed to position sites very well with content only created via artificial intelligence..
By the way, at the beginning of 2023, Google changed its mind and said that it now accepts AI-generated content, as long as it’s useful, original, and high quality.
As you can see, testing is very important in SEO and it will allow you to detect what works well or not so well on your pages. For example, a simple change in the wording of a title tag can allow you to increase your click-through rate, and therefore the traffic on your page.
I hope you enjoyed all these tips and that you will apply them at home as soon as possible! Do you have any other tips to share with WPMarmite readers?
Tell us all about it in the comments area.
Receive the next posts for free and access exclusive resources. More than 20,000 people have done it, why not you?





Continue reading
Articles posted in WordPress TipsThe ultimage guide to WordPress maintenance
Do you want to be hacked? Do you want to have a slow site like a turtle? Do you want to be unable to restore your site? If you answer “yes,” you are a kamikaze. A little birdie tells me…
Gutenberg vs. page builder: Which to choose?
On my left, Gutenberg. On my right, a page builder. In the center, you. Gutenberg draws you in. He holds out his arms. And yet no: This page builder still has a few choice features that make you love it….
16 ways to make money on the internet with WordPress in 2024
“How to make money on the internet with WordPress? Here we go, another clickbait title!” I can hear you from here, dear readers. Let me be clear: far be it from me to fall into the trend of those websites…